The Power of Polyphenols

What are Polyphenols?
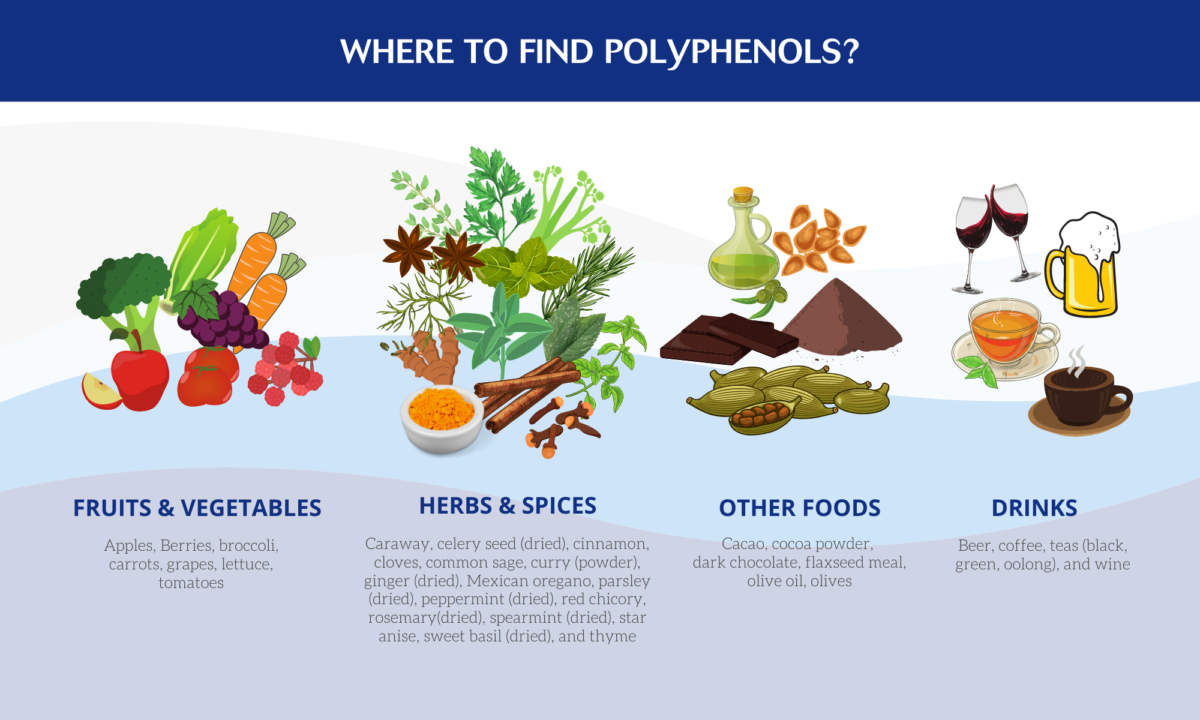
Polyphenols are phytonutrients that can be found in certain plant foods such as fruits, vegetables, herbs, spices and seeds.
These micronutrients give the plants their specific dark red, purple or blue, vivid colors and are known for their numerous health benefits such as reducing oxidation and inflammation in the body, supporting immunity and a healthy cardiovascular system. They are also known to help with weight issues and diabetes.
In order for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties to be released, polyphenols have to be consumed and ingested by the bacteria in our gut. Their consumption in return supports the growth of healthy bacteria and a balanced microbiome.
There are many types of polyphenols, however most of the ones we consume, such as anthocyanins, come from the flavonoids group of polyphenols.
Anthocyanins are water-soluble colored pigments that give a rich dark and vivid red-purple color to fruits and vegetables. They are found for example in berries, particularly blueberries and blackberries, or red grapes.
Mostly known for their strong antioxidant properties, they protect cardiovascular capillaries and promote venous return.
They also improve the contractile function of blood vessels as inflammation is reduced.
They are also used to support the capillaries of the scalp to prevent hair fall and support hair growth. Indeed often, hair fall is linked to poor circulation in the blood vessels at the surface of the scalp.
Our products with polyphenols
Following a balanced diet with plant based products rich in polyphenols will surely have great health benefits. It will help your body fight free radicals and inflammation, support a healthy cardiovascular system, and promote a healthy gut.
However, while polyphenols display a wonderful and wide range of health benefits, these phytochemicals are sensitive and the way they are consumed may impact the polyphenol content of the food you eat. For example, the polyphenol content of onions will greatly decrease once they are cooked. Using the microwave or high-temperature cooking modes like frying will also reduce the content of beneficial phenolic compounds in the food.
While watching your diet to include polyphenol sources, it may be useful to support your body with natural supplements that will provide a bioavailable source of polyphenols, readily available for your body to use for optimal action.
We recommend supplements that are gastro protected, to maintain the integrity of the active ingredients until their point of absorption.
Sources:
[1] USDA. USDA database for the flavonoid content of selected foods. 2003.
[2] Gatta L., « Experimental single-blind study: 60 pts with venous insufficiency received bilberry extract equivalent to 173 mg anthocyanins daily of placebo for 30 days », Fitoterapia, 1988, 115:109-116.[3]Kay CD, Holub BJ. The effect of wild blueberry (Vaccinium angustifolium) consumption on postprandial serum antioxidant status in human subjects[4]Kay CD, Holub BJ. The effect of wild blueberry (Vaccinium angustifolium) consumption on postprandial serum antioxidant status in human subjects[5] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/polyphenols#benefits[6] https://www.livescience.com/52524-flavonoids.html[7] https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/polyphenols#benefits
[8] https://www.livescience.com/52524-flavonoids.html






